
-

联系电话
热线电话
+86-15221725700
-
添加微信
微信扫一扫添加

-
回到顶部
联系我们

动物实验低压氧舱(加大版)
产品描述
动物实验低压氧舱用于模拟低压氧高原环境,压力可以根据需要自行设置,最高可模拟海拔高度12000米,适用于更多的鼠笼或中小型动物如犬、猴、兔、鼠等。
整个实验装置由动物舱体、真空系统、监测及控制系统构成。设备的自动化程度高,无须专人守候,可长期持续一个月运行。
产品描述
多功能
实时显示海拔和氧气浓度动态变化曲线
多功能编程控制:可进行阶段式、周期式、循环模式控制
实验过程数据可保存至U盘,可在电脑读取分析
具备自动换气功能,符合动物饲养规范
提供多方位的报警功能,提醒实验人员异常状态
确保安全
从设计开始到最终完成测试和检查,所有实验氧舱都遵循严格的生产过程;
具有紧急关闭和自动排气系统,以适应各种情况。
动物舱体
主体采用进口亚克力加厚材质,坚固可靠,透明方便观察;
铝合金及不锈钢材料支撑;
具有脚轮脚刹设计,方便移动。
气体输送控制系统
高性能低噪音的真空系统,为系统提供稳定的压力;
具有气体缓冲器,减小甚至消除了细股急流气体对小动物的影响;
完善的多级空气过滤器,确保动物舱内气体不会污染实验环境。
拓展及特殊定制
动物生理指标监测
可实现的监测指标:心电图、心率、体温、血压、呼吸、血氧饱和度;
呼吸代谢监控功能
采血给药功能
视频监测功能
动物低氧跑台装置
低氧强迫游泳装置
温控功能
恒温功能,温度可控制,室温-40℃;
低温功能,4℃,温度可控制,室温-4℃;
可定制其它功能
应用领域
高原医学研究、肺水肿、脑水肿、肺动脉高压等疾病研究
型号说明
名称 | 型号 | 说明 |
动物实验低压氧舱 | ProOx-810 | 舱内尺寸(长×直径):700×560mm |
动物实验低压氧舱 | ProOx-810L | 舱内尺寸(长×直径):1200*800mm |
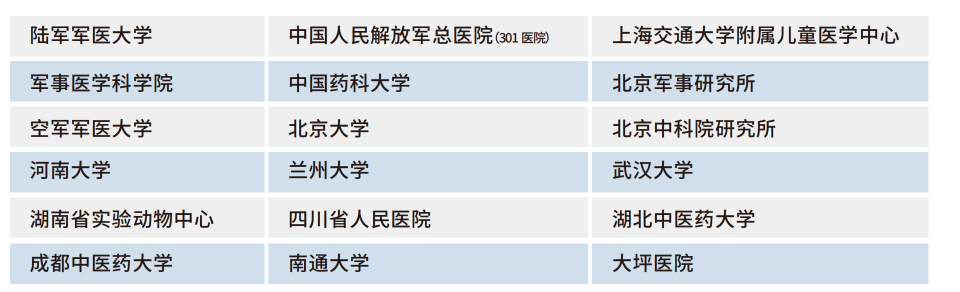
客户名单(部分)
相关文献
[1] Drekolia M K, Mettner J, Wang D, et al. Cystine import and oxidative catabolism fuel vascular growth and repair via nutrient-responsive histone acetylation[J]. Cell Metabolism (IF 30.9), 2025.
[2] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang C Y, et al. Inactivation of AXL in Cardiac Fibroblasts Alleviates Right Ventricular Remodeling in Pulmonary Hypertension[J]. Advanced Science (IF 14.1), 2025: e08995.
[3] Lei R, Gu M, Li J, et al. Lipoic acid/trometamol assembled hydrogel as injectable bandage for hypoxic wound healing at high altitude[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal (IF 13.4), 2024, 489: 151499.
[4] Li Z, Li H, Qiao W, et al. Multi-omics dissection of high TWAS-active endothelial pathogenesis in pulmonary arterial hypertension: bridging single-cell heterogeneity, machine learning-driven biomarkers, and developmental reprogramming[J]. International Journal of Surgery (IF 10.1), 10.1097.
[5] Pei Y, Huang L, Wang T, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells loaded into hydrogel/nanofiber composite scaffolds ameliorate ischemic brain injury[J]. Materials Today Advances (IF 10), 2023, 17: 100349.
[6] Wang Q, Liu J, Li R, et al. Macrophage κ-opioid receptor inhibits hypoxic pulmonary hypertension progression and right heart dysfunction via an SCD1-dependent anti-inflammatory response[J]. Genes & Diseases (IF 9.4), 2025: 101604.
[7] Wang Y, Zhang R, Chen Q, et al. PPARγ Agonist Pioglitazone Prevents Hypoxia-induced Cardiac Dysfunction by Reprogramming Glucose Metabolism[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 2024, 20(11): 4297.
[8] Wang Y, Shen P, Wu Z, et al. Plasma Proteomic Profiling Reveals ITGA2B as a key regulator of heart health in high-altitude settlers[J]. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics, 2025: qzaf030.
[9] Lan Y, Zhao S, Song Y, et al. Physicochemical properties of selenized quinoa protein hydrolysate and its regulatory effects on neuroinflammation and gut microbiota in hypoxic mice[J]. Journal of Future Foods, 2025.
[10] Pan Z, Yao Y, Liu X, et al. Nr1d1 inhibition mitigates intermittent hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via Dusp1-mediated Erk1/2 deactivation and mitochondrial fission attenuation[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2024, 10(1): 459.
[11] Zhou Y, Ni Z, Liu J, et al. Gut Microbiota‐Associated Metabolites Affected the Susceptibility to Heart Health Abnormality in Young Migrants at High‐Altitude: Gut Microbiota and Associated Metabolites Impart Heart Health in Plateau[C]//Exploration. 2025: 20240332.
[12] Li C, Zhao Z, Jin J, et al. NLRP3-GSDMD-dependent IL-1β Secretion from Microglia Mediates Learning and Memory Impairment in a Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-induced Mouse Model[J]. Neuroscience, 2024, 539: 51-65.
[13] Yang W, Li M, Ding J, et al. High-altitude hypoxia exposure inhibits erythrophagocytosis by inducing macrophage ferroptosis in the spleen[J]. Elife, 2024, 12: RP87496.
[14] You Z, Huang Q, Zeng L, et al. Rab26 promotes hypoxia-induced hyperproliferation of PASMCs by modulating the AT1R-STAT3-YAP axis[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2025, 82(1): 1-16.
[15] Pei C, Shen Z, Wu Y, et al. Eleutheroside B Pretreatment Attenuates Hypobaric Hypoxia‐Induced High‐Altitude Pulmonary Edema by Regulating Autophagic Flux via the AMPK/mTOR Pathway[J]. Phytotherapy Research, 2024, 38(12): 5657-5671.
[16] Duan H, Han Y, Zhang H, et al. Eleutheroside B Ameliorates Cardiomyocytes Necroptosis in High-Altitude-Induced Myocardial Injury via Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway[J]. Antioxidants, 2025, 14(2): 190.
[17] Song J, Zheng J, Li Z, et al. Sulfur dioxide inhibits mast cell degranulation by sulphenylation of galectin-9 at cysteine 74[J]. Frontiers in Immunology, 2024, 15: 1369326.
[18] Jia N, Shen Z, Zhao S, et al. Eleutheroside E from pre-treatment of Acanthopanax senticosus (Rupr. etMaxim.) Harms ameliorates high-altitude-induced heart injury by regulating NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2023, 121: 110423.
[19] Huang Q, Han X, Li J, et al. Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2025, 17(3): 341.
[20] Wu Y, Tang Z, Du S, et al. Oral quercetin nanoparticles in hydrogel microspheres alleviate high-altitude sleep disturbance based on the gut-brain axis[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 2024, 658: 124225.
[21] Zhou Z, Zhao Q, Huang Y, et al. Berberine ameliorates chronic intermittent hypoxia‐induced cardiac remodelling by preserving mitochondrial function, role of SIRT6 signalling[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2024, 28(12): e18407.
[22] Shang W, Huang Y, Xu Z, et al. The impact of a high-carbohydrate diet on the cognitive behavior of mice in a low-pressure, low-oxygen environment[J]. Food & Function, 2025, 16(3): 1116-1129.
[23] Pei C, Jia N, Wang Y, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 protects against hypobaric hypoxia-induced high-altitude pulmonary edema by inhibiting apoptosis via ERK1/2-P90rsk-BAD ignaling pathway[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2023, 959: 176065.
[24] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[25] Ding Y, Liu W, Zhang X, et al. Bicarbonate-Rich Mineral Water Mitigates Hypoxia-Induced Osteoporosis in Mice via Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Pathway Regulation[J]. Nutrients, 2025, 17(6): 998.
[26] Gu N, Shen Y, He Y, et al. Loss of m6A demethylase ALKBH5 alleviates hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension via inhibiting Cyp1a1 mRNA decay[J]. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 2024.
[27] Luan X, Zhu D, Hao Y, et al. Qibai Pingfei Capsule ameliorated inflammation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) via HIF-1 α/glycolysis pathway mediated of BMAL1[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 2025, 144: 113636.
[28] Jiang H, Lu C, Wu H, et al. Decreased cold‐inducible RNA‐binding protein (CIRP) binding to GluRl on neuronal membranes mediates memory impairment resulting from prolonged hypobaric hypoxia exposure[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2024, 30(9): e70059.
[29] Chang P, Xu M, Zhu J, et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of Mitochondrial Division Attenuates Simulated High‐Altitude Exposure‐Induced Memory Impairment in Mice: [30] Involvement of Inhibition of Microglia‐Mediated Synapse Elimination[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(6): e70473.
[30] Liu C, Qu D, Li C, et al. miR‐448‐3p/miR‐1264‐3p Participates in Intermittent Hypoxic Response in Hippocampus by Regulating Fam76b/hnRNPA2B1[J]. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 2025, 31(2): e70239.
[31] Wu L W, Chen M, Jiang D J, et al. TCF7 enhances pulmonary hypertension by boosting stressed natural killer cells and their interaction with pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells[J]. Respiratory Research, 2025, 26(1): 202.
[32] Xie L, Wu Q, Huang H, et al. Neuroregulation of histamine of circadian rhythm disorder induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2025: 177662.
[33] Cai S, Li Z, Bai J, et al. Optimized oxygen therapy improves sleep deprivation-induced cardiac dysfunction through gut microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2025, 15: 1522431.
[34] Wang X, Xie Y, Niu Y, et al. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signal mediates M1-type microglia and accelerates high-altitude-induced forgetting[J]. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience, 2023, 17: 1189348.
[35] He Y, Wang Y, Duan H, et al. Pharmacological targeting of ferroptosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary edema: therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 through activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2025, 16: 1644436.
[36] Guo Y, Qin J, Sun R, et al. Molecular hydrogen promotes retinal vascular regeneration and attenuates neovascularization and neuroglial dysfunction in oxygen-induced retinopathy mice[J]. Biological Research, 2024, 57.
[37] Liu L, Zhang J, Song S, et al. Paraventricular nucleus neurons: important regulators of respiratory movement in mice with chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Annals of Medicine, 2025, 57(1): 2588664.
[38] Ma Q, Ma J, Cui J, et al. Oxygen enrichment protects against intestinal damage and gut microbiota disturbance in rats exposed to acute high-altitude hypoxia[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2023, 14.
[39] Lan J, Lin J, Guo Y, et al. Sequencing and bioinformatics analysis of exosome-derived miRNAs in mouse models of pancreatic injury induced by OSA[J]. Frontiers in Physiology, 2025, 16: 1712442.
[40] Feng X, Li C, Zhang W, et al. Mechanism of retinal angiogenesis induced by HIF-1α and HIF-2α under hyperoxic conditions[J]. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): 36049.
[41] Yao Y, Chen Y, Li Y, et al. TGM2 Enhances Hypobaric Hypoxia-mediated Brain Injury Via Regulating NLRP3/GSDMD Signaling[J]. Neurochemical Research, 2025, 50(6): 1-11.
[42] Yang A, Guo L, Zhang Y, et al. MFN2-mediated mitochondrial fusion facilitates acute hypobaric hypoxia-induced cardiac dysfunction by increasing glucose catabolism and ROS production[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects, 2023: 130413.
[43] Chu H, Jiang W, Zuo N, et al. Astrocyte activation: A key mediator underlying chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive dysfunction[J]. Sleep Medicine, 2025: 106692.
[44] Xu A, Huang F, Chen E, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy attenuates heatstroke-induced hippocampal injury by inhibiting microglial pyroptosis[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2024, 41(1): 2382162.
[45] Zhang Z, Zheng X, He Y, et al. Hyperbaric oxygen ameliorates neuroinflammation in heat-stressed BV-2 microglial cells: potential involvement of EAAT2 regulation[J]. International Journal of Hyperthermia, 2025, 42(1): 2583133.
[46] Jinyu F, Huaicun L, Yanfei Z, et al. Nogo-A Protein Mediates Oxidative Stress and Synaptic Damage Induced by High-altitude Hypoxia in the Rat Hippocampus[J]. 2024.
[47] Su L, Ni T, Fan R, et al. An attention to the effect of intravitreal injection on the controls of oxygen-induced retinopathy mouse model[J]. Experimental Eye Research, 2024, 248: 110094.
[48] Xu Y, Xu J, Li J, et al. Interplay of HIF-1α, SMAD2, and VEGF signaling in hypoxic renal environments: impact on macrophage polarization and renoprotection[J]. Renal Failure, 2025, 47(1): 2561784.
[49] Zhang D, Bian W, Gao Z. Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Endometrial Function in Female Rats: Mechanism Exploration[J]. Nature and Science of Sleep, 2025: 2485-2499.
[50] Zhang N, Wei F, Ning S, et al. PPARγ Agonist Rosiglitazone and Antagonist GW9662: Antihypertensive Effects on Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Hypertension in Rats[J]. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 2024: 1-13.
[51] Zhang Y, Zhang A, Yang J, et al. Hypoxic Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosome‐Derived SLC25A3 Ameliorates Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Modulating Macrophage Polarization and Oxidative Stress[J]. Cell Biochemistry and Function, 2025, 43(12): e70152.
[52] Lan J, Wang Y, Liu C, et al. Genome-wide analysis of m6A-modified circRNAs in the mouse model of myocardial injury induced by obstructive sleep apnea[J]. BMC Pulmonary Medicine, 2025, 25(1): 158.
[53] Zhang L, Liu X, Wei Q, et al. Arginine attenuates chronic mountain sickness in rats via microRNA-144-5p[J]. Mammalian Genome, 2023, 34(1): 76-89.
[54] Wei J, Hu M, Chen X, et al. Hypobaric Hypoxia Aggravates Renal Injury by Inducing the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway[J]. Current Medical Science, 2023: 1-9.
[55] Zhang L, Li J, Wan Q, et al. Intestinal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate necrotizing enterocolitis injury[J]. Molecular and Cellular Probes, 2025, 79: 101997.
[56] Liao Y, Ke B, Long X, et al. Abnormalities in the SIRT1-SIRT3 axis promote myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through ferroptosis caused by silencing the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway[J]. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders, 2023, 23(1): 582.
[57] Wang M, Wen W, Chen Y, et al. TRPC5 channel participates in myocardial injury in chronic intermittent hypoxia[J]. Clinics, 2024, 79: 100368.
[58] Li J, Ye J. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease mouse model via postsynaptic mechanisms[J]. Sleep and Breathing, 2024: 1-9.
[59] Binbin L I, Haizhen L I, Houhuang C, et al. Utilizing Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy to Improve Cognitive Function in Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease by Activating Autophagy-Related Signaling Pathways[J]. Physiological Research, 2025, 74(1): 141.
[60] Han J, Wang L, Wang L, et al. 5-Hydroxytryptamine Limits Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Progression by Regulating Th17/Treg Balance[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2025, 48(5): 555-562.
[61] Nan L, Kaisi F, Mengzhen Z, et al. miR-375-3p targets YWHAB to attenuate intestine injury in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis[J]. Pediatric Surgery International, 2024, 40(1): 63.
[62] Liu B, Zheng W, Tang C, et al. Scutellarein-containing novel formula attenuates hypoxia through inhibiting apoptosis[J]. 2025.
参考研究
高原疾病介绍
不同的海拔高度大气压和氧分压的变化对比
*我公司可提供3Q验证,根据客户的特殊应用、特殊需求提供功能定制服务,也可以提供相关的实验服务,详情请来电咨询。
*此介绍及参数为产品基础信息,可能滞后于产品更新,具体参数请与我司联系。